AI and Data Protection: How Artificial Intelligence Safeguards Your Privacy
Discover how AI protects your personal and business data. Learn about AI-powered cybersecurity, privacy ethics, and real-world data protection tools in this complete guide.
Published on 10 Nov 2025

Can AI Keep Your Data Safe? Everything You Need to Know
Each and every click, message and search you do leaves behind data, your digital fingerprint. However, with the increasing size of our online world, cyber threats are also increasing. Can Artificial Intelligence keep that data safe, or is it another risk to occur?
AI is changing the manner in which we guard, observe and control data. AI data protection is taking center stage in ensuring information safety by identifying suspicious activities as well as preventing cyberattacks before they occur. However, it also brings up new concerns regarding privacy, transparency and ethics.
Therefore, is AI capable of keeping you safe? Let's discuss.
What is AI data Security?
AI data protection/security describes the application of AI technology to ensure that digital data remains undiscovered, lost, or abused by unauthorized personnel. The use of sophisticated algorithms and machine learning helps it to detect risks at a higher rate than conventional methods.
For example:
- In cases where hackers attempt to log-in to your bank account, AI cybersecurity identifies anomalies in the pattern of logging in.
- The AI systems in hospitals can secure patient data by encrypting files and alerting of any unauthorized access.
- Cloud service providers can detect suspicious data flows that might indicate a breach with the help of AI.
The issue of AI data security lies not in the protection only, but in the prediction. It can work through millions of data rows, forecasting the possible attacks in order to enable organizations to act before it is too late.
How AI detects and prevents cyber threats
Sophisticated criminals exist now more than ever. They employ sophisticated software, spoof emails and social engineering gimmicks to steal personal or business data. To resist such emerging threats, AI cybersecurity assists in the fight, as it can perform tasks that humans are not able to, including processing large volumes of data in a short period of time and identifying minor indications of attacks.
The way AI identifies and eliminates cyber threats is as follows:
Real-Time Monitoring
Artificial intelligence monitors traffic and actions of users all the time. When it detects any sudden alterations, such as unusual places of log-ins or big file transfers, it sends warnings to security teams in real time.
Pattern Recognition
AI gets to learn how normal behavior is. Where it does not fit that pattern, it is considered suspicious.
Automated Response
AI may automatically do something that blocks a user, disconnects, or isolates infected systems to limit further destruction.
Learning from Past Attacks
Machine learning enables AI to retain attack patterns. When a hacker has attempted the similar technique, the system notices it and blocks it at a faster rate.
Phishing Detection
AI cybersecurity will search emails and websites to identify red flags that could indicate fraud, including unrealistic URLs or the discrepancy between domains, to minimize the threat of fraudulent schemes.
AI Ensuring data protection
AI has a significant contribution at various levels of cybersecurity. The following are some of the main measures that it takes to secure data:
Threat Detection and Real Response
AI detects possible threats earlier as compared to conventional tools. It prevents malware, ransomware and data breaches prior to spreading.
Fraud Prevention
Banks and other e-commerce businesses use AI to identify suspicious transactions or spending, avoiding online fraud.
Cloud and Network Security
AI can ensure protection of large-scale cloud networks by scanning data flow, revealing weak spots, and stopping harmful traffic.
Identity Verification
Facial recognition, biometrics and voice identification are implemented through AI to ensure that only those with authority can use sensitive systems.
AI Data Protection
AI cybersecurity aids in the protection of data, encrypted access control, and automatic data classification—such that confidential information remains secure and confidential.
With the help of these layers, AI creates a network that is continuously, proactively, and adaptively safe.
How Businesses Use AI for Data Security
In the digital world, security of information is of utmost importance. Now, companies are using AI-based cybersecurity in order to identify threats, avoid data leaks, and maintain customer trust. Second, AI tools can sift through large volumes of data, detecting risks at a more rapid rate than a human.
Finance: Fraud Detection
Banks apply AI data protection to identify the pattern of transactions and alert fraud in real time. As an example, when a payment appears suspicious, AI systems help prevent money loss by blocking it out before money is lost in case of online fraud—this is one aspect that helps financial firms combat online fraud.
Healthcare: Data Encryption
Hospitals keep patient data safe with AI privacy and security applications. AI encrypts data, grants access, and traces abnormal behavior, conforming to the privacy law and ensuring the safety of sensitive health data.
Retail: Checking of Identity
Retailers utilize AI to get the customer accounts. Online shopping is safer and more secure, as AI cybersecurity will confirm the logins, detect fake profiles, and prevent unauthorized access to payment information.
Other Industries
AI is used by manufacturers, schools, and governments to protect intellectual property, avert phishing, and prevent cyberattacks.
Benefits of AI in data protection
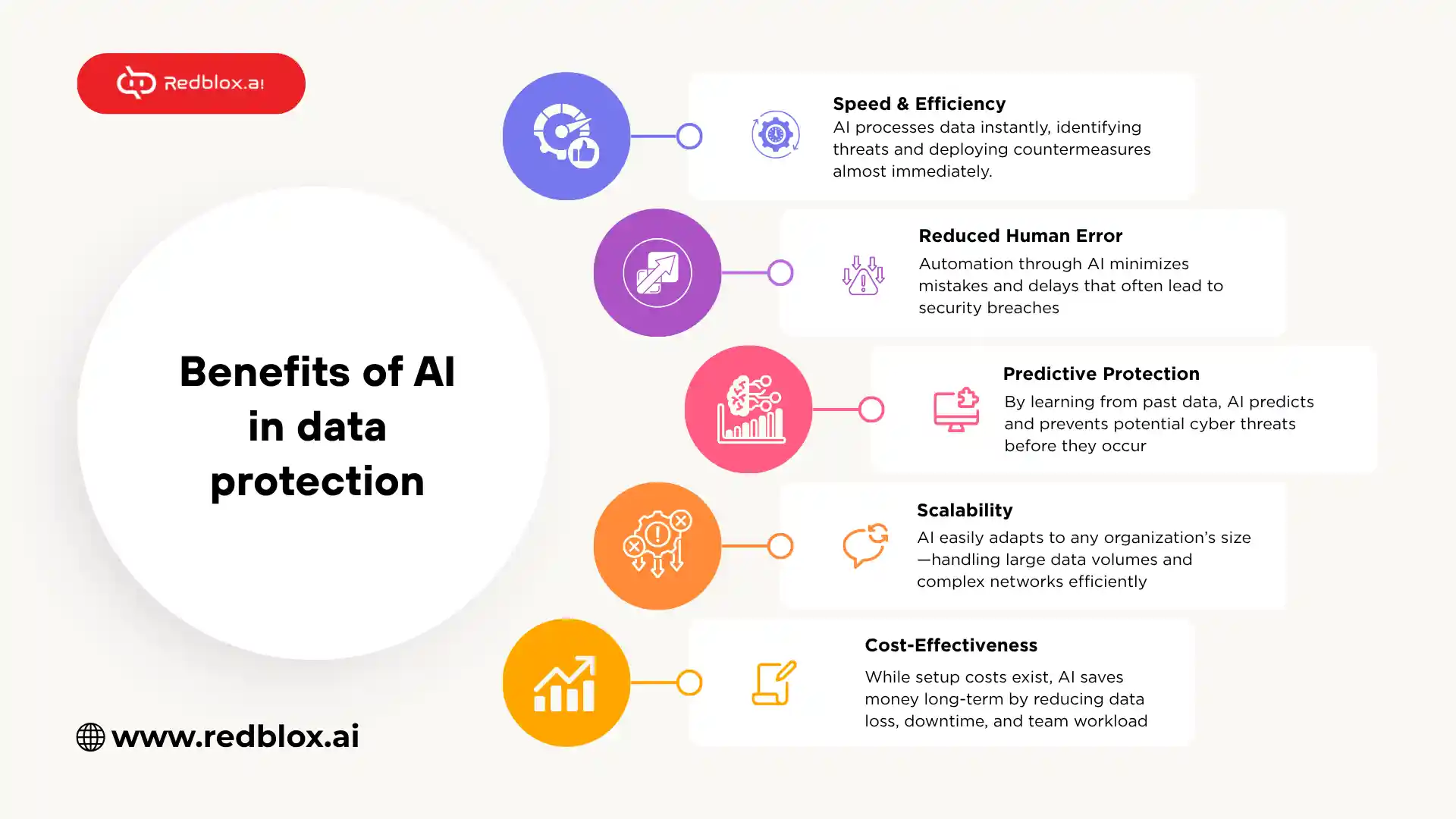
To sum up, AI cybersecurity does not replace human specialists; it empowers them, providing the team with smarter tools with which to secure sensitive information more successfully.
Challenges in AI based Security system
Although AI is a powerful tool, it is not an extraordinary one. The challenges that should be considered include
False Positives
In other cases, AI raises false alarms due to harmless practices being recognized as dangerous.
Bias in Algorithms
The training data may be biased, which can be passed to AI systems. This may result in inequitable rulings, particularly where the systems are identity-based.
High Implementation Costs
The construction and the upkeep of AI-based security can also prove a bit expensive, particularly to small enterprises.
Data Privacy Concerns
In order to be useful, AI tends to require access to large amounts of user data; this raises the question of privacy and control.
Dependence on Quality Data
AI can be as good as the data that it is being trained on. Poor quality of data may result in weak protection or incorrect results.
AI is an excellent ally, yet it should be created with the concepts of AI privacy and security in mind. When used without the necessary controls, the same technology that was being used to safeguard information accidentally revealed personal information.
AI Security Vs Traditional Cybersecurity
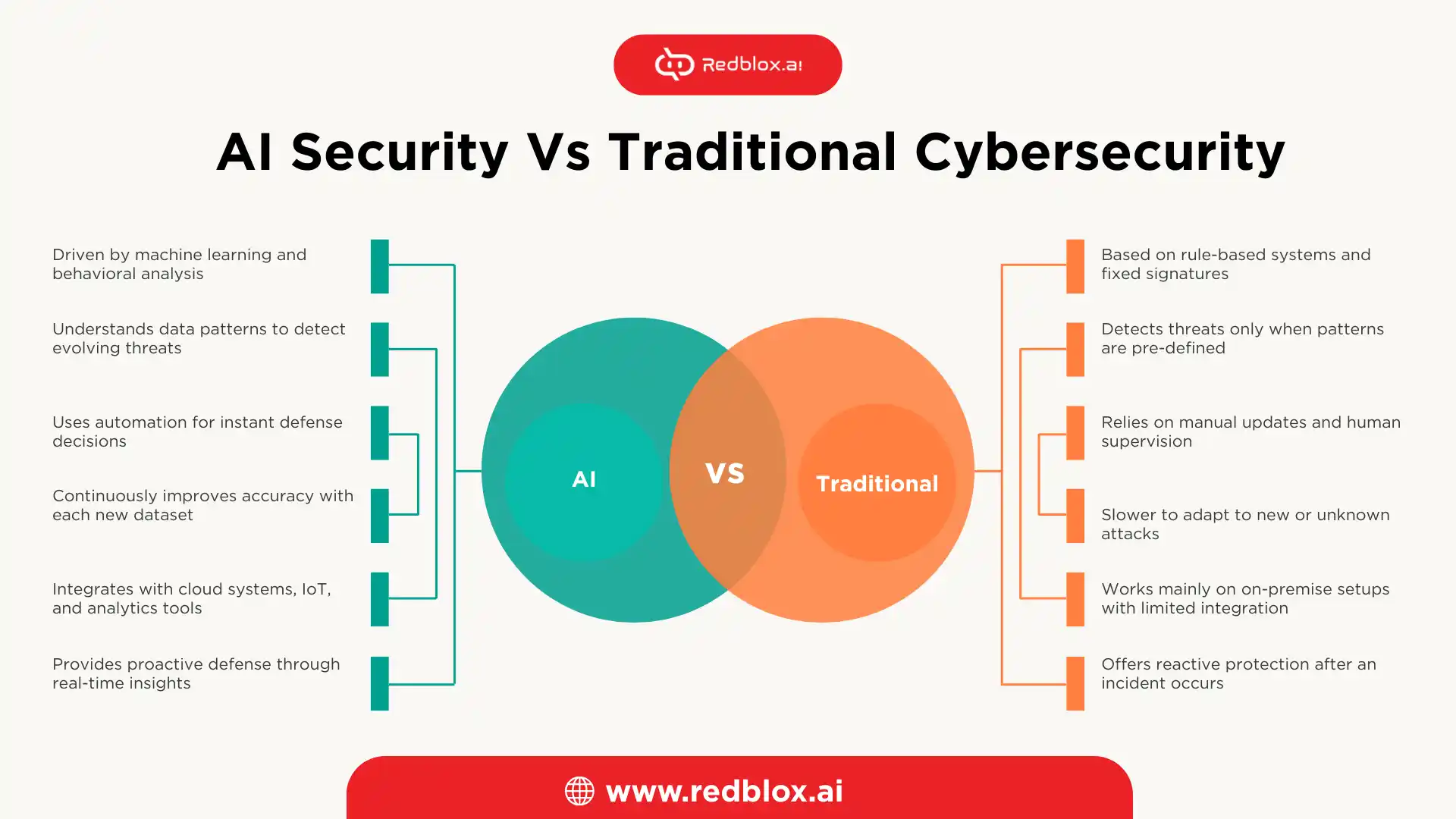
Real-World Examples
To take some examples of AI in data security currently employed by large companies, consider the following:
IBM Watson to Cybersecurity
Relies on AI to process large volumes of data on security reporting and extract the patterns that could possibly be indicators of threats.
Darktrace
An example of a company in the United Kingdom that applies machine learning to identify the presence of abnormal network behavior in real time.
Google's Gmail AI
Blocks spam/phishing emails (more than 99.9% per day) by scanning billions of emails.
PayPal
Relying on AI to identify fraudulent transactions through customer behavior and transaction history.
Explore our AI development at Redblox.ai
What Happens to the Information you share with AI
When you search with AI applications such as chatbots, picture generators, or online assistants, it can be assumed that your data can be:
- Saved in the meantime to enhance AI.
- Trains models (based on the policy of the tool).
- Disclosed to third-party vendors in case of an integration.
This does not necessarily imply that your personal information is revealed. Reliable AI systems utilize high encryption, anonymize information and conform to privacy regulations.
As a user, you may do the following steps to ensure that you are safe:
- The privacy policy should be read prior to using an AI tool.
- Do not exchange personal, financial or confidential data.
- Select AI services with the possibility of an opt-out in the storage or reuse of data.
- Use the local or enterprise AI models, which do not transmit your data to the external servers.
The first step to being in control in the age of AI data protection is to acquire a way of understanding how your data is used.
What data you should never share with AI
Financial Information
Banking information, credit cards, and investments have to be confidential.
Health Data
Do not provide sensitive medical or mental information unless it is on a proven health care system.
Proprietary Business Information
Strategies, contracts or intellectual property of a company might be misused or leaked.
Authentication Codes or passwords
They are unnecessary to AI models, as they can lead to the compromising of accounts.
In any case, AI systems should be regarded as open spaces. When you will not post it on the open platform, you should not feed it to an artificial intelligence tool.
How to secure data in AI System
Data Encryption
Encode the data on the rest and in transmission. This way web attackers will be unable to read your information in case they get it.
Access Control
Only authorized users should have access to data.
Regular Audits
Always check AI systems against vulnerabilities and ensure that they have the most recent security patches.
Anonymization
Remove personal identifiers from datasets before feeding them to AI training.
Ethical AI Policies
Follow AI privacy ethics by establishing distinct principles regarding data collection, data use and storage.
Use Trusted AI Platforms
Select platforms that have a good reputation for compliance with AI privacy and security.
CTA: Intend to secure your data using AI? Call our AI team at Redblox Technologies to create secure and smart systems.
The future of data in AI Security
The future of the use of AI in data protection is bright. With the future development of AI, it will be able to predict and prevent cyber threats even more. It will come up with some future developments such as
Explainable AI
Systems that are capable of articulating their decisions enhance transparency and accountability.
Quantum-Safe Encryption
The methods of encryption that resist the future attacks by quantum computers.
Zero-Trust Frameworks
Models of security in which no one, including internal users, is automatically trusted.
AI Collaboration
The next generation of AI tools will exchange information in all industries to avoid international cyber terrorists.
AI can potentially be the ultimate defense of humanity in the digital age due to its constant refinement and ethical design.
Conclusion
AI is turning around the way in which we secure our information. It is transforming all aspects of cybersecurity, starting with threat detection and moving to encryption and privacy tracking. Nevertheless, as much as AI enhances the privacy and security of AI, it still requires responsible use, openness, and user awareness.
Although AI can anticipate, detect, and stop threats, human beings have major roles in influencing it ethically. The combination of intelligent technology and human decisions is the most effective.
FAQ
What is AI data security?
The security of AI data follows the method of artificial intelligence designed to ensure that sensitive data is not hacked or abused by someone. It identifies abnormal behavior and deters and protects data with intelligent algorithms.
How does AI keep the personal data safe?
AI secures personal data by detecting threats in time, encrypting personal information, and preventing suspicious access. It is trained through previous attacks to make it more secure, yet human eyes will be required so that mistakes do not happen and privacy is not compromised.
How can the data I give to AI devices be used?
Your data can be stored or trained with the help of external AI tools. The privacy policy should always be read, and no one should provide their personal information, such as passwords, bank details, or personal files, without the tool ensuring data security.
What are the examples of AI in data security?
The examples are AI detecting phishing emails, monitoring fraud, and facial recognition as a means of accessing information securely. With AI, Big tech companies can scan networks to prevent cyberattacks automatically.
What are the ways I can ensure the security of my data with AI?
Use reliable AI applications, passwords and two-factor authentication. Sharing personal data should be avoided, systems should be maintained, and privacy settings should be revised regularly to remain safe.