Autonomous AI Agents: How They Make Smart Decisions
Learn how autonomous AI agents plan, reason, use memory, and recover from errors to make intelligent decisions—and how businesses can deploy them safely.
Published on 01 Dec 2025

How AI Agents Make Smart Decisions in Complex Situations
Autonomous AI agents are on the front line, and AI is developing at a rapid pace. These agents, unlike the simple chatbots, are able to plan, reason, remember, correct mistakes and even solve conflicting tasks. However, what about smart decisions when things are dynamic or complicated?
It is simplified in this guide to explain how AI agents can solve the tasks previously requiring a human brain.
What Is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is a digital worker. It is not only able to answer questions; it can solve problems. It perceives a task, divides it into steps, acts with the help of tools, and learns based on what succeeded or failed and changes its plan when it becomes necessary.
In contrast to traditional software, which does not operate under any fixed rules, such as "if X occurs, do Y," and so on, an AI agent operates in a flexible way: it will comprehend the circumstances, will plan actions, will attempt to perform these actions, will verify the outcomes, and will learn over time. It becomes possible with the help of such sophisticated tools such as LLMs, memory systems, integrations, and decision-making algorithms.
Why Businesses Use AI Agents
- They accelerate the processes and save up to 40% on manual labor.
- They cope with marketing, customer service, finances, human resources, logistics, etc.
- They are capable of embracing change and just solving complicated issues automatically.

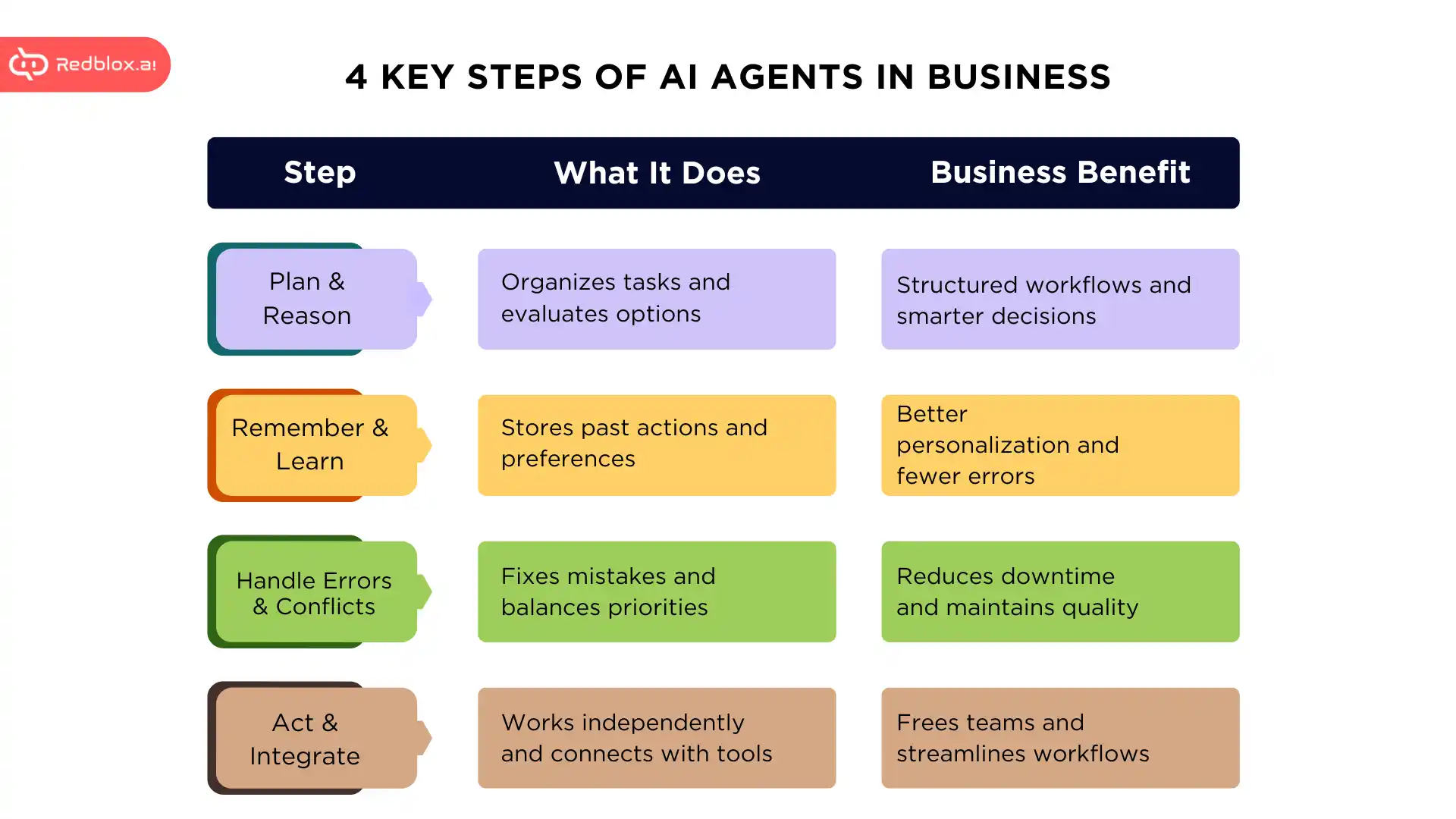
How AI Agents make Smart Decisions
Now, we can deconstruct the abilities that enable the agents to work in complex environments.
Planning: Mapping multisteps
Planning refers to the act through which the agent establishes an effective map of action prior to action. Humans can be doing this by default when resolving problems, and AI agents can imitate this ability.
When an agent is given a task such as to come up with a comprehensive social media plan for our winter sale, it does not immediately translate to posting of the content. Rather, it develops a systematic strategy. It recognizes the aim, splits it into activities, gets to know what information is lacking, makes decisions about which tools to utilize, and plans the work.
How AI Agents Usually Plan Despite the fact that each system is unique, the vast majority of agents employ a planning loop, i.e.,
Getting to know what the user really desires
- Breaking the goal into steps
- Selecting the correct tools
- Calculating the required effort
- Anticipating possible challenges
That is why autonomous AI agents can have long workflows that are not limited to simple text generation.
The importance of Planning in Business.
A retail business that intends to host a festival campaign, a restaurant that is going to create a schedule of weekly meals, or an HR department that hires new staff all need systematic steps. By following structured planning, agents can speed up tasks by 30%.
Reasoning: Comparing alternatives
The agent has the capacity to think logically, which is called reasoning. It assists the system to compare various alternatives and select the best alternative. An agent will tend to get stuck or act randomly without any justification.
Types of Reasoning Agents Use
Although agents do not think in the human style, they have other reasoning styles:
- Deductive logic: A is the case, and B is the case that has to be true, and thus C must as well be true.
- Inductive reasoning: Learning through patterns and historic examples.
- Abductive reasoning: A best guess in the face of incomplete data.
- Multi-step reasoning: Problems with multiple steps, which are related to each other
An example of this is the best shipping path to a logistics firm. It takes into account the weather, the distance, the cost, the traffic, and the urgency when determining the route. It is one of the real-world examples of AI agents working on tasks that require thoughtful consideration.
The role played by Reasoning in making decisions
When a user requests, "Make my product more visible online," then the agent will not limit by making a single ad. It reasons through:
- What the target audience is
- Which platforms work best
- What past data says
- What are the tools that are capable of running campaigns?
- What timeline works It is this reasoning capacity that enables businesses to trust agents.
Memory: Short-term, long-term memory
An essential part of the AI agents is memory. In its absence, every interaction would be fresh, and the agent would make repeated errors.
An agent may have different kinds of memory:
- Conversation memory in the short term
- Long-term stored knowledge
- User preferences and user profile
- Knowledge in uploaded documents
- Tool memory (tool prior experiences or API experience)
Why Memory Changes Everything
Think about a customer that is always willing to use environmentally friendly products. A memory agent will recollect this and make personalized subsequent recommendations. This skill is useful in the creation of continuity, trust, and relevance.
It also enables autonomous AI agents to learn from past tasks and reduce repeated tasks by 25%. As an example, when an agent prepares reports on a weekly basis, it will learn the favorable format, tone, and structure without being prompted to do so.
Error Handling: detecting, retry, fallback, learning
There are no clean-cut situations in the real world. The APIs crash, data disappears, tools crash, and user instructions are occasionally unclear. The strong AI agent should be knowledgeable regarding how an error can be detected and corrected without affecting the whole process.
Mistakes that AI Agents are prone to
- API failures
- Tool output errors
- Missing information
- Low-confidence responses
- Malformed inputs
- Timeouts or system delays
How Agents Fix Errors
A capable agent will:
- Detect the error
- Retry the steps
- Alternate method that is used
- Ask the user for more info
- Store the failure in memory
- Adjust future approaches
This skill is critical in the application of AI agents for business, which reduces mistakes by 20%, particularly in an industry such as finance or operations, where errors can be very expensive.
Conflict Resolution: Multi-Agents collaboration
The agents are subject to conflicting priorities. As an example, the customer support agent has to answer quickly but provide correct and safe information. A marketing agent might be forced to balance a budget constraint and the desire to have maximum coverage.
How Agents Handle Conflicts
Agents are usually guided by a hierarchy of rules or a priority map. Their decision-making is based on impact, safety, accuracy, policy, and goals. To illustrate, speed is never higher than the level of accuracy in giving legal advice.
Multi-agent systems also find use in conflict resolution, where a number of agents collaborate. A single agent could be in charge of research, another write the material, and another audit compliance. They should remain on the same track and not be conflicting.
Real Business Use Cases
Intelligent AI agents are employed in real-world systems.
Weekly Financial Report Automation
If a mid-sized firm was manually processed, it could take 90% of the time weekly.
An agent was created to:
- Gather transaction data
- Check accuracy
- Highlight anomalies
- Format reports
- Send emails to leaders
This saved time by 26% and also minimized the human errors. Because the system did not require any supervision, it is a good example of autonomous AI agents and the way these can minimize the workload.
Customer Support Scale
An example of this is a telecommunication company that put a machine in place to handle the increasing number of queries. It dealt with first-level queries, plan upgrades, outage check and tracking of complaints.
The agent was able to enhance performance as time went on and provide consistent responses with the help of memory and reasoning. This contributes to the expanding list of on-the-job real-world examples of AI agents assisting customer support departments to perform more effectively.
AI Agent Frameworks: Intelligent Agent Construction by Developers
The system architecture supports every powerful agent, such as AI agent frameworks, which commonly offer planning, reasoning, memory and execution tools available to the developers.
These frameworks contain such features as
- Long-term memory modules
- Tool integration
- Retry and error logic
- Planning engines
- Secure access
- Monitoring dashboards
The selection of the appropriate framework will make an agent more reliable and scalable.
Why Frameworks Matter
An efficient framework simplifies the process in case a firm desires to employ agents alongside CRMs, cloud storage, payment options, and messaging services. In its absence, developers would take huge amounts of time to create everything on their own.
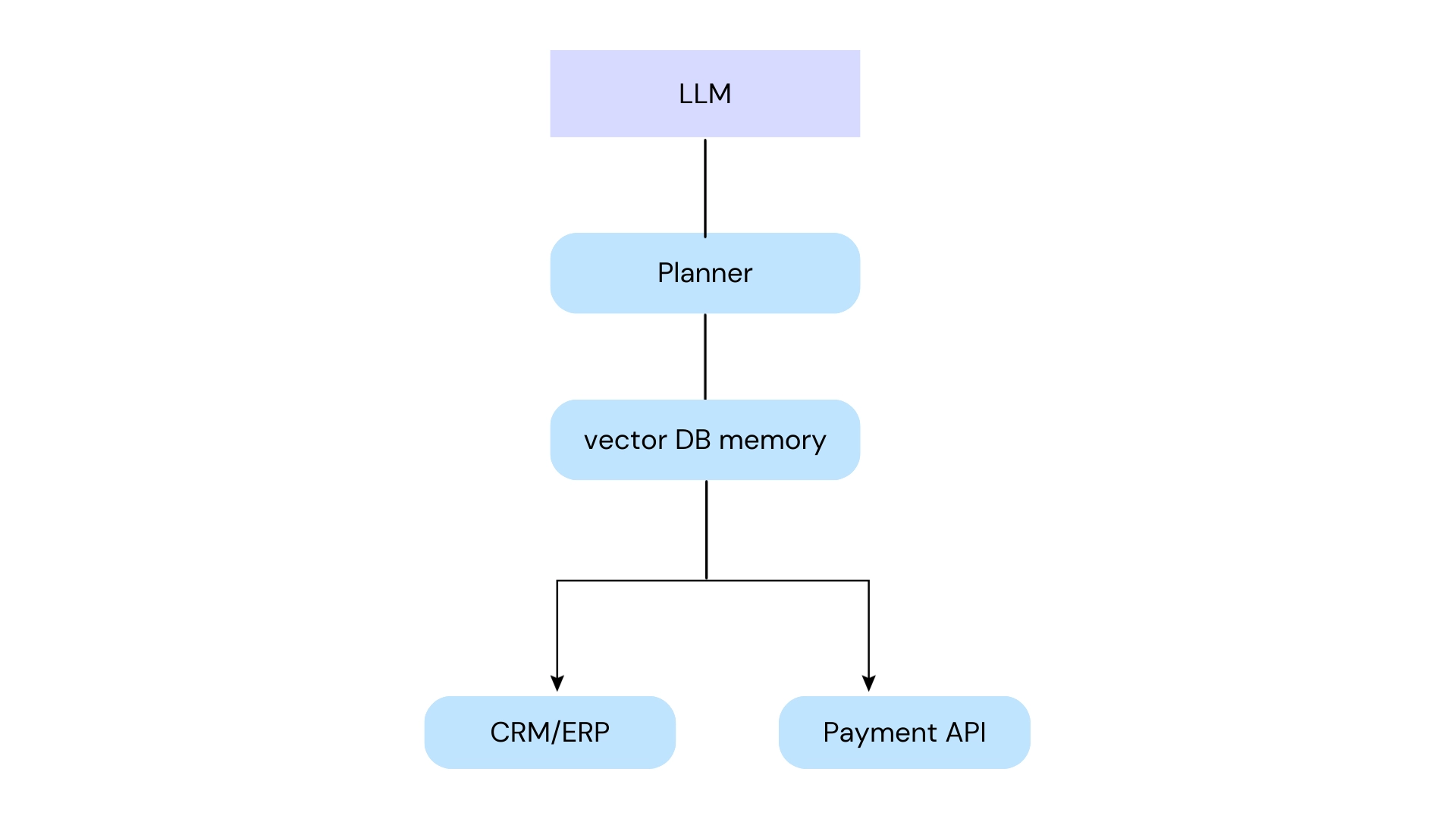
Technical Foundations
Technical specifications are a common feature looked at by companies investing in AI agents prior to deployment.
Ordinary Technical Aspects Involve:
- LLM options like GPT, Llama and Claude
- Vector database for memory
- Data encryption
- Audit logs and policies
- API integration capability
- Latency and speed
- Cost per run
- Confidence scoring
- Observability dashboards
These specifications assist teams to determine the safety, scalability and reliability of a system. They also establish the possibility of risk-free management of sensitive data by AI agents serving businesses.
Security & Compliance (privacy, audit logs, RBAC) Risk
The implementation of autonomous AI agents also makes the deployment more efficient, yet it raises the issue of critical security and compliance concerns. There should be powerful controls to safeguard data, enforce traceability, and restrict approvals.
- Privacy: Make sure that sensitive information of agents is encrypted, is as anonymous as possible, and is operated in accordance with regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Audit Logs: Have clear and unalterable records that capture what agents do, assist in incident investigations, and hold them accountable.
- RBAC: Use full role-based access controls to ensure that agents have least-privilege access to reduce the chances of unauthorized access or manipulation of systems
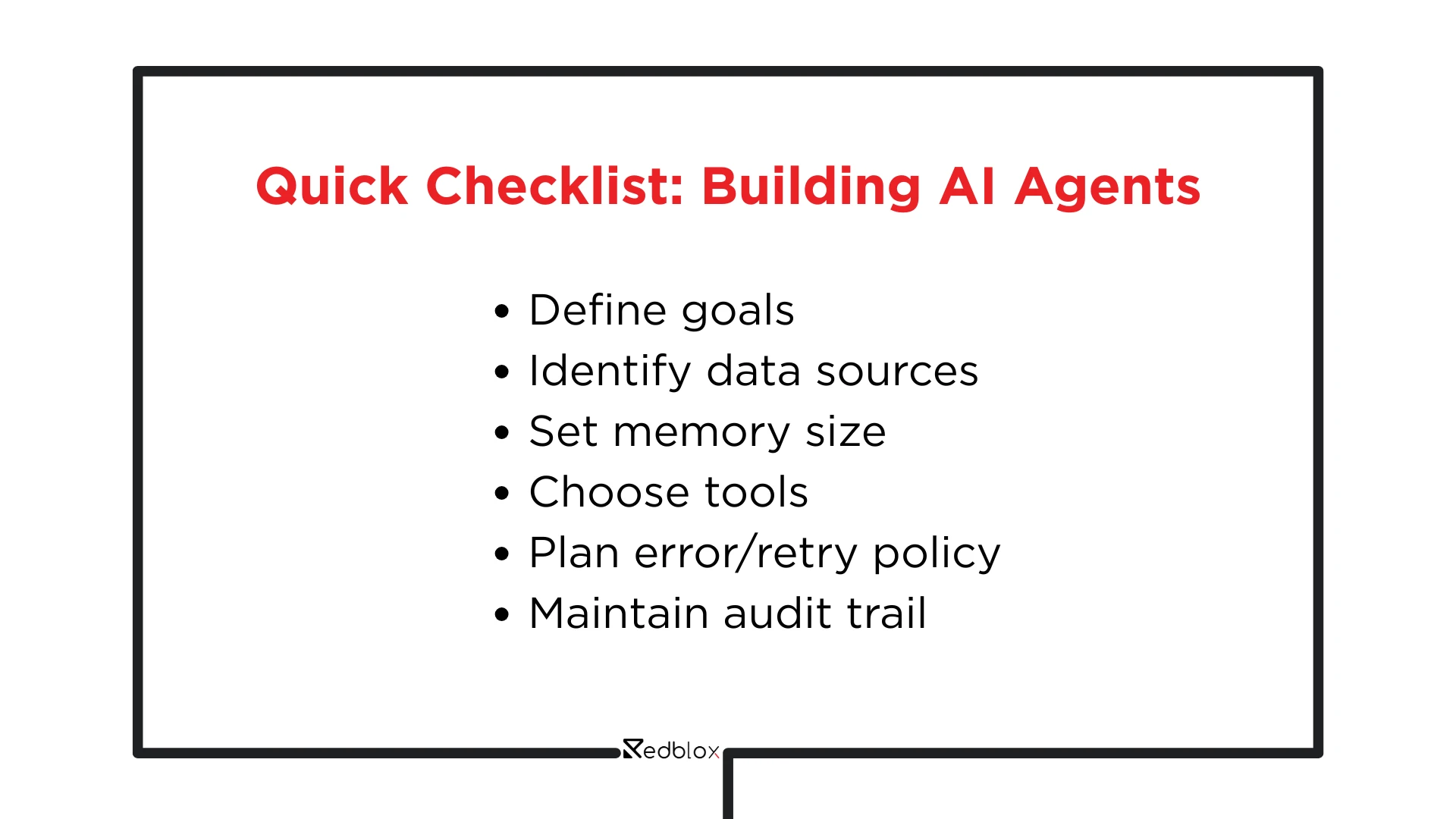
How to deploy AI agent to your organization
To show us the usual steps that companies take in developing an agent, we shall discuss it step-by-step.
Goal Definition: This could be decreasing the time of waiting on support, automating invoice generation, better marketing uniformity or creating reports.
System development: systems are selected based on trusted AI agent frameworks. This provides the agent with a base on which it can have memory, planning, and integrated tools.
Memory layer: This will contain a collection of vectors, documents that have been stored, preferences of their users, and policy rules. This memory is required to ensure accuracy and context on the part of the agent.
Tools installation: CRMs, payment systems, communication channels, and other APIs. The agent is able to perform actual actions rather than just reply in text.
Testing: Teams assess the agent's behavior regarding errors, conflicts, ambiguous orders, and incomplete data. Powerful systems are self-adjusting.
Companies gradually roll out autonomous AI agents to actual work based on testing. They are assigned small tasks and keep track of records as real-life examples of AI agents.
As time passes, the workflow is streamlined, and the agent is eventually assigned additional work.
The AI Agent Future of Growth
AI agents will introduce even greater opportunities in the future. Multi-agent teams will be present whereby the agents will collaborate but each perform different tasks. The memory will be more profound and accurate. The reasoning skills will be enhanced using superior models. It will have even easier integration with standard business tools.
Businesses will become dependent on digital departments to be run by powerful autonomous AI agents going behind the scenes continuously.
The early adopters of this will have huge efficiency and decision-making advantages in their business.
Final Thoughts
The use of AI agents is transforming the nature of organizational work. They are able to think, plan, remember and correct mistakes as humans, but quicker. They can be trusted to be effective digital assistants with the appropriate design, equipment, and security.
Autonomous agents for enterprise can automate whole processes using the appropriate knowledge and AI agent models.
FAQ
1. How do AI agents make smart decisions in complex situations?
The intelligent choices of AI agents are based on the analysis of data, the evaluation of outcomes, and the choice of actions that will maximize their objectives. They apply methods such as reinforcement learning, probabilistic modeling and dynamic planning to manage uncertainty and respond to changes in the environment.
2. What algorithms help AI agents work in uncertain or unpredictable environments?
The algorithms that AI agents use include Bayesian inference, fuzzy logic, the Monte Carlo algorithm, and reinforcement learning. These algorithms assist agents to make estimations on probabilities, handle incomplete information and select the most appropriate choice even in circumstances that are uncertain.
3. How do reinforcement learning agents choose the best action?
Reinforcement learning agents are the agents that interact with the environment, test actions and learn as a result of a reward signal. They revise their policies with time to make decisions that will always yield the greatest reward in the long term, making them smarter in situations that are dynamic and complex.
4. Why is context important for AI decision-making?
Context provides AI agents with the background to make correct decisions. These memory modules, embeddings and representations of state enable the agents to trace the previous actions and results. This makes them know patterns, predict, and respond to new situations.
5. How do multiple AI agents coordinate decisions in the same system?
Various artificial intelligence agents interact via shared communication protocols, distributed planning and collaborative learning approaches. They can negotiate, divide resources or adjust to the behavior of each other, and this will enable them to solve complicated problems like robotics teamwork or traffic optimization.
6. Can AI agents explain the decisions they make?
Yes. Most explainable AI tools, such as attention maps, decision traces, model summaries, or SHAP values, are utilized by many AI agents. These methods expose the rationale of the activities of the agent, and its decision-making is more open, understandable, and credible.